IT is becoming more essential to every company
Information technology (IT) is becoming increasingly critical and strategically significant for businesses of all sizes. It is essential for organizations to develop an IT vision and strategy that aligns seamlessly with their business goals, ensuring that technology not only supports but actively drives business agility and innovation. Directors, managers, and advisors must navigate complex questions about digital transformation, cybersecurity, and IT infrastructure to maintain a competitive edge. The integration of emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing is key to creating a robust and future-proof IT landscape that can adapt to evolving market demands.
What are IT and ICT? Some definitions
The terms IT and ICT are often used interchangeably. Yet, they mean different things. IT stands for Information Technology while ICT means Information and Communication Technology. As the names imply, they are very closely related.
- Information Technology refers to the complete information domain, which covers hardware, software, devices, and networks. Their purpose is to store, protect, retrieve, and process electronic data to support company processes. This field encompasses a wide swathe of sub-specialties.
- The term Information and Communication Technology is often used to emphasize that telecommunication and media also belong to the information domain.
For ease of use and consistency’s sake, this website uses the term IT.
Current IT issues
- What do digital disruption and digital transformation really mean? What does it mean for your company, and how can you give this topic a place in your company’s IT vision and ICT strategy?
- How can you ensure that your company can adapt quickly, embracing new IT technologies quickly, effectively, and efficiently in order to stay ahead of the competition?
- What IT governance, IT competencies, and ICT organization do you need in the future to be able to support your business processes? The growth of new application platforms and functionalities has to be given a place in the organization.
- How can you prevent being overrun by separate “Application Cloud” initiatives and solutions that cause compartmentalization, which will impede effective and efficient cooperation?
- How can information technology be used to make dashboards and predictive analyses? Decision-makers need to be informed about the progress of the company strategy and ICT strategy.
Thanks to our wealth of experience, Passionned Group can support companies in the development of a future-proof, tailored IT vision and strategy.
Learning from the IT past
Our unique IT vision is the foundation of our approach. We’re experts when it comes to data-driven, smart, agile organizations. Our experience has given us insight into emerging IT trends, which form the cornerstones of digital disruption. The IT domain of every company is confronted with a new turning point, from a historical perspective. All the more reason to reinvent your company’s IT vision and IT strategy.
The 4 stages: a historical perspective on information technology
IT has become a lot more important for every company in recent years. This growing importance can be explained by the stages of development that companies have undergone. The image below displays the 4 stages.

Every company has undergone multiple stages of providing IT services. Every stage roughly covers a five-year period, but they’re getting progressively shorter. They can’t be precisely pinned down to a time frame as every company entered the next stage at a different point.
Develop an ICT vision
The desired role of information technology is shifting from service provider to business enabler and digital transformation advisor. To be able to play this part optimally in the future, new competencies are required in the IT organization. These competencies are essential:
- Change management
- (IT) Innovation
- Agile & scrum working
- Business Process Management
- Data management & Business Analytics
- Security and Architecture
In the past, 90% of internal IT resources were invested in running the business, and 10% in innovation. But now, these ratios need to be flipped. 90% should be spent on innovation and business alignment, and 10% on running the business.
Infrastructure has become a commodity
In order to achieve this change, it may prove very helpful or essential to outsource infrastructure services or use cloud-based solutions. Infrastructure services have become a commodity, not unlike gas, water, and electricity, and service partners can provide cost-efficient solutions at scale, thanks to their size. This allows the internal IT organization to focus entirely on the development of:
- New business models: you can use various methods to define and describe your revenue model. The most well-known is the business model canvas. It describes how the business operates and generates revenue in 9 blocks. Read more about business models.
- Lean business processes: Lean may be the quintessential improvement method. It improves your operational excellence, customer intimacy, and product leadership.
- E-workstyle: a combination of new application functions and more attention for specific and novel IT sub-specialties that lead to an effective and efficient e-workstyle.
- Data analytics: more professional use of available data and information to steer your organization better and become more agile. Read more about data science and analytics.
The 25 most important trends in IT
The speed and frequency of new developments in the IT domain are rapidly increasing. The image below displays the most important developments that companies and IT have to face, but it’s by no means all-encompassing. The most important trends are:
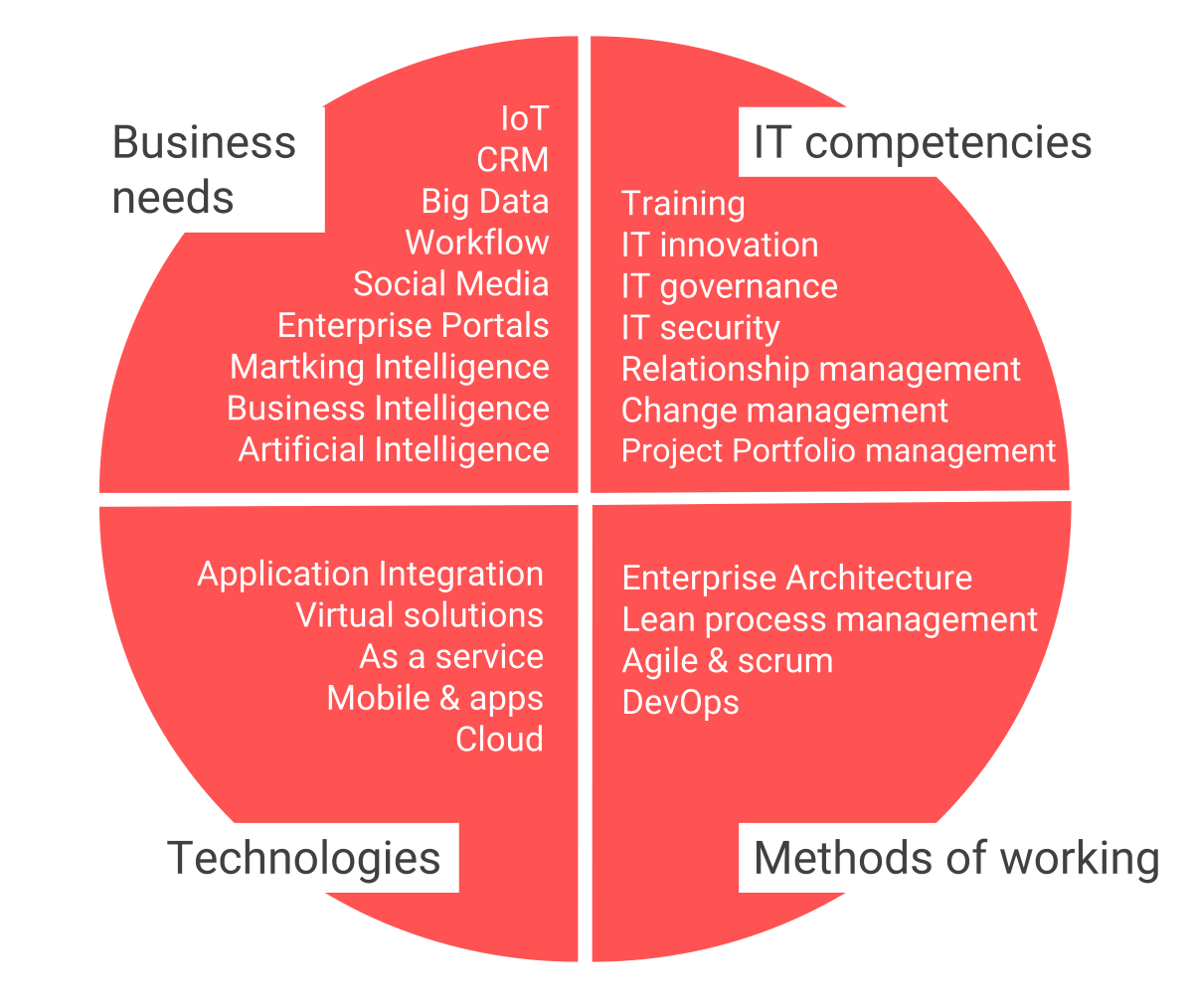
1. IoT
Internet of Things is the name given to devices that connect to the internet. This enables new possibilities for companies to provide improved or additional services, such as:
- Proactive and more efficient device maintenance, thanks to the device communicating information about its operational status.
- Remote and corrective device maintenance.
- Remote monitoring and device control.
- Remote expansion of (software) functionality of devices in the field.
2. CRM
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system offers an integrated set of functionalities in sales, marketing, and service. These departments build and maintain a customer profile that enables your company to better meet their needs and improve customer relations. This translates into added value and more revenue. Centrally registering customer data and interactions isn’t the goal, but the starting point to analyze where improvements can be made.
3. Big Data
Big Data is the collective name for the phenomenon of the rapid increase in the amount of available data generated by (for example) social media, the Internet of Things, and internal systems generating unstructured data. This data potentially contains a treasure trove of information, if companies can perform smart data analyses.
4. Workflow management
Paper procedures are inefficient, so they should be transformed into digital workflows. The advantages include better lead times, more insight, and eliminating search times. Some examples: travel requests, investment requests, personnel requests, processing declarations, etc.
5. Social media
Social media allows companies to perform more precisely targeted marketing than traditional marketing. Potential benefits include:
- Increased name recognition.
- Targeting specific demographics and leading them to your website or apps.
- Gathering public opinion as input for the improvement of products and services.
- Gathering reviews and likes to get ahead of the competition.
6. Enterprise portals
Enterprise portals are gateways for customers and partners to interact with the business. These portals support various processes: from requesting and sharing information to ordering and providing services. Customers and partners can access their information through protected gates.
7. Marketing Intelligence
Marketing Intelligence policies and processes take care of the structural collecting and analyzing of information about the market in which the company operates. There are specific MI tools for this. The goal isn’t to spread the gathered information as news for management. Based on further analysis of the information, you can make substantiated suggestions about how the company should react to external events. This can affect the 6 Ps: product, price, place, promotion, personnel, and presentation.
8. Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence concerns the structured collection and analysis of internal and external data and information. The goal is to make the company make better business decisions. BI systems are the foundation of the analyses. Thanks to self-service BI tools, the focus of IT is shifting to the business. The better the information and the analyses, the better the decisions that lead to growth and improve the company’s competitive edge.
9. Artificial Intelligence
AI applications learn from input of, and interaction with, people. Because of this, fewer people are needed. Some examples of applications are customer service functions, initial reviews of job applications, and applications in monitoring situations. Ethics play a very important role in AI.
10. E-learning
By using e-learning, new software training courses can be much more efficient and effective. The trainer only has to make a lesson plan once and document it on video, and trainees can watch or repeat it whenever they want to. Testing, control, and feedback can be part of an e-learning environment.
11. IT innovation
The speed with which new technologies and solutions become available will only increase further. To prevent your company’s competitive edge from slipping, it’s essential to structurally invest in IT innovation and to experiment with the application of emerging IT trends.
12. IT governance
Good cooperation between business and ICT is essential to make organizations more agile and decisive as is deciding on priorities for software development. The efforts that have to be made on the business side are still too often underestimated.
13. Cybersecurity
Cybercrime is making headlines every day. Companies have to do more to arm themselves against this threat. Not just by using more IT security technology, but also by increasing employees’ awareness and changing their attitudes and behavior.
14. Relationship management
Relationship management is about receiving structural feedback about the scope and quality of provided services. Ensuring customer and user satisfaction and preventing shadow IT are important motivating factors.
15. Change management
The speed with which organizations can adopt new processes and systems is becoming more of a bottleneck than the development of new software. It’s crucial to focus on the soft side of change too, like attitude, behavior, energy, motivation, and developing competencies.
16. Project portfolio management
With project portfolio management, you can directly guide the potential and ongoing business and IT projects required by your business strategy. Reporting isn’t the end goal, but a means of facilitating decision-making and optimizing the quality, speed, and added value of projects.
17. Enterprise Architecture
The goal of Enterprise Architecture is to ensure that the arrangement of your applications, data, and technical infrastructure are aligned with your business goals and processes. Making a detailed architecture plan shouldn’t be a goal in and of itself. They have to support communication with business and IT colleagues about desired solutions, overlap, and grey and white spots that have to be dealt with. The de facto standard for Enterprise Architecture is TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework).
18. Lean Process Management
Lean process management is about continuously improving business processes, and reducing waste and inefficiency, by looking from the customer’s perspective. A de facto standard is the Lean Six Sigma method.
19. Agile & scrum
This is a newer method for faster software development, and is the counterpart of the traditional waterfall method. The waterfall method is based on the phases defining, developing, testing, using, and aftercare. The scrum method is based on an iterative process with sprints of a maximum of 3 to 4 weeks, which deliver several functionalities.
20. DevOps
DevOps is a lean vision and method of integrating software development and maintenance teams, instead of separating them into silos. This leads to increased decisiveness and the ability to react more quickly to customer feedback.
21. Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
This concerns technology to efficiently exchange information between various business applications. This is often designated as “middleware”. With a good application integration architecture, you can register data once, at the source, and “automatically” share it and reuse it in other business applications.
22. Virtual Solutions
Virtualization can occur on the levels of workplace, server, storage, and network. Some important advantages of virtualization:
- More simple/transparent replacement of physical equipment.
- More efficient administration of a central management layer over multiple physical devices.
- Optimization of resources used across multiple physical devices.
- Separating network traffic in order to prioritize and guarantee the performance of different business applications.
In a virtual workplace, for example, all the business applications and data are no longer stored on the decentralized device, but they run centrally in a data center.
23. As a service
As a service is a designation for data, applications, infrastructure, and IT security applications that can be run in the public cloud. There are different variants, such as:
- PAAS (Platform as a Service, for example, ERP or CRM platforms that run in the cloud);
- SAAS (software as a service, for example, collaboration tools that run in the cloud);
- and IAAS (Infrastructure as a Service, for example, server capacity available through the public cloud);
- and SECAAS (Security as a Service, for example, an IT security tool, like intrusion detection and prevention (IDS/IPS) that runs in the cloud).
24. Mobile & apps
The use of cellphones and apps is increasing more than the use of PCs. Customers and colleagues increasingly want to do things on phones that they used to do on PCs. The advantages are self-evident. Quicker and easier information requests, inputs, ordering, paying, etc.
25. Cloud
There’s a distinction between private and public Cloud. Private Cloud means business applications and infrastructure run in a centralized data center, owned by the company. They control all the hardware and software, as well as the location of the data center. Public Cloud means using hardware and software stored in the Cloud through a subscription service. The vendor owns the hardware and software and determines which data centers run which applications, as well as where the data is stored.
The above trends have to be structured and prioritized based on the company’s IT vision and strategy. That’s the only way to ensure that you’re doing the right things in the right order, and to become and stay smart, agile, and competitive.
Our approach for better IT
Many companies struggle to determine where to start and how to pivot. By performing a structured analysis – through workshops, which enable us to effectively and efficiently gather information – Passionned Group can help your company to make a custom IT vision and IT strategy that suits your needs. Naturally, we can provide services in any of the areas above separately, such as digital disruption and IT innovation, Business Intelligence, Big data, Data science, IT Governance, ICT organization, or process management.
If you want one of our experienced interim managers to lead the planning and execution phases, we can meet your needs. Contact us for more information.
About Passionned Group
 Passionned Group is the specialist in data analytics and everything that comes with it. Our experienced IT experts help organizations in the transition to an intelligent, data-driven organization. Every other year we organize the Dutch BI & Data Science Award™.
Passionned Group is the specialist in data analytics and everything that comes with it. Our experienced IT experts help organizations in the transition to an intelligent, data-driven organization. Every other year we organize the Dutch BI & Data Science Award™.


